- Battery Manufacturing Equipment
- Battery Laboratory Assembly Equipment
- Battery Pack Assembly Equipment
- Sodium Ion Battery Manufacturing Equipment
- Solid State Battery Assembly Line
- Dry Electrode Assembly Equipment
- Supercapacitor Assembly Equipment
- Perovskite Solar Cell Lab Equipment
- Li ion Battery Materials
- Ni / Al / Cu Metal Foam
- Customized Electrode
- Cathode Active Materials
- Anode Active Materials
- Coin Cell Parts
- Lithium Chip
- Cylindrical Cell Parts
- Battery Current Collectors
- Battery Conductive Materials
- Electrolyte
- Battery Binder
- Separator and Tape
- Aluminum Laminate Film
- Nickel Strip/Foil
- Battery Tabs
- Graphene Materials
- Cu / Al / Ni / Stainless steel Foil
- Battery Laboratory Equipment
- Li ion Battery Tester
- Battery Safety Tester
- Battery Material Tester
- Film Coating Machine
- Rolling Press Machine
- Electrode Mixer
- Coin Cell Crimping Machine
- Coin Cell Electrode Disc Punching
- Pouch Cell Sealing Machine
- Pouch Cell Stacking Machine
- Pouch Cell Forming Machine
- Pouch Cell Ultrasonic Welder
- Pouch Cell Electrode Die Cutter
- Cylinder Cell Sealing Machine
- Cylinder Cell Grooving Machine
- Electrode Slitting Machine
- Cylinder Cell Winding Machine
- Cylinder Cell Spot Welding Machine
- Electrolyte Filling
- Type Test Cell
- Other Battery Making Machine
- NMP Solvent Treatment System
- Vacuum Glove Box
- Lab Furnaces
- Ball Mill
- Hydraulic Press
- Laboratory Equipment
blog
Battery Production Line
- 2024-10-09
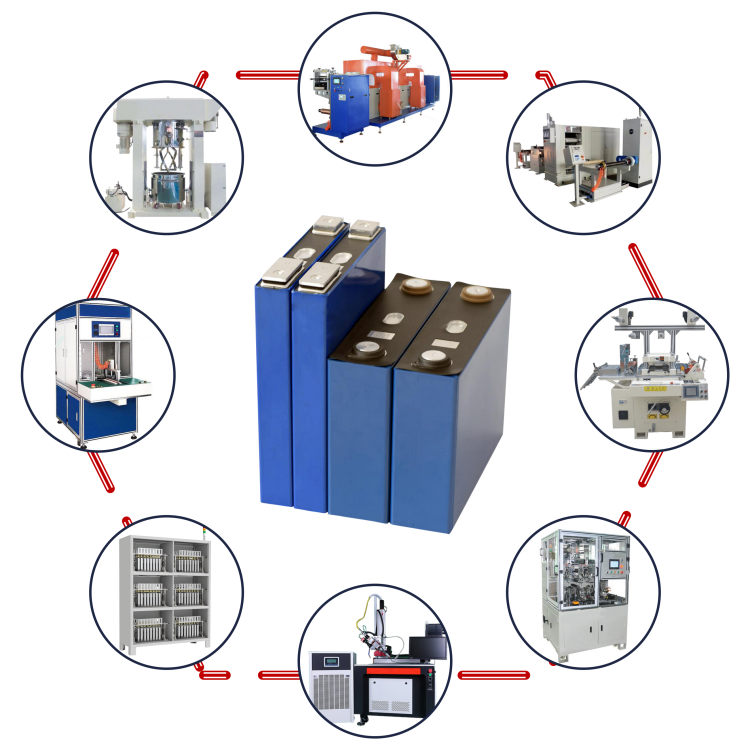
Battery Production Line: Overview and Key Components
A battery production line is a highly automated manufacturing setup designed to produce various types of batteries, including lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride, and lead-acid batteries. These production lines are critical in meeting the growing demand for batteries in applications such as electric vehicles (EVs), consumer electronics, renewable energy storage, and industrial applications.
● Key Processes in a Battery Fabrication Line
1. Material Preparation
- Active Material Mixing: The active materials for electrodes (such as lithium compounds for cathodes and graphite for anodes) are mixed with binders and conductive additives to form slurries.
- Separator Production: Separators, which prevent short circuits between electrodes, are produced from materials like polyethylene or polypropylene.
2. Electrode Fabrication
- Coating: The slurry is coated onto metal foils (copper for anodes and aluminum for cathodes) using precision electrode calendering machines to achieve uniform thickness.
- Drying: Coated electrodes are dried in ovens to remove solvents, ensuring optimal performance characteristics.
- Calendering: The dried electrodes are compressed to enhance density and improve conductivity.
3. Electrode Cutting
- The dried and calendered electrodes are cut into specific dimensions suitable for the battery design.
4. Cell Assembly
- Layer Stacking or Winding: The anode, separator, and cathode are assembled by stacking or winding them together, depending on the cell design (cylindrical, prismatic, or pouch).
- Electrolyte Filling: The electrolyte is injected into the cell, saturating the electrodes and separator for optimal ion flow.
- Sealing: Cells are sealed to prevent leakage and contamination, often using heat sealing or ultrasonic welding.
5. Formation and Aging
- Formation Cycling: The cells undergo initial charging and discharging cycles to activate the electrochemical materials, stabilizing performance.
- Aging: Cells are aged in controlled environments to ensure consistent long-term performance.
6. Testing and Quality Control
- Performance Testing: Each battery is tested for key metrics such as capacity, internal resistance, voltage, and cycle life to ensure they meet specifications.
- Safety Testing: Rigorous safety tests, including thermal runaway, short-circuiting, and overcharging, are conducted to ensure compliance with safety standards.
7. Packaging and Shipping
- Once the batteries pass all quality checks, they are packaged and prepared for shipment to customers or distribution centers.
● Key Equipment in a Battery Production Line
1. Mixers: For preparing electrode slurries.
2. Coating Machines: For applying active material slurries onto metal foils.
3. Drying Ovens: To remove solvents from coated electrodes.
4. Calendering Machines: For compressing electrodes to desired specifications.
5. Cutting Machines: For precise sizing of electrodes.
6. Assembly Stations: For stacking or winding the electrodes, separators, and electrolytes.
7. Filling Machines: For injecting the electrolyte into the cells.
8. Sealing Equipment: To secure the cell and prevent leakage.
9. Testing Equipment: For performance and safety evaluations.
● Advantages of a Battery Production Line
1. Automation: High levels of automation improve efficiency, reduce labor costs, and minimize human error.
2. Scalability: Production lines can be scaled up or down to meet changing demand, making them flexible and adaptable.
3. Quality Control: Integrated testing and quality control processes ensure that only high-quality batteries reach the market, enhancing reliability and safety.
4. Cost Efficiency: Streamlined processes reduce production costs and waste, making it economically viable to produce batteries at scale.
● Applications of Batteries
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Batteries are a critical component, providing the energy needed for propulsion and energy recovery.
- Consumer Electronics: Used in smartphones, laptops, tablets, and wearable devices.
- Renewable Energy Storage: Batteries store energy from renewable sources like solar and wind, ensuring a stable energy supply.
- Industrial Applications: Employed in backup power systems, robotics, and various industrial equipment.
● Conclusion
A battery production line is a highly automated manufacturing setup designed to produce various types of batteries, including lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride, and lead-acid batteries. These production lines are critical in meeting the growing demand for batteries in applications such as electric vehicles (EVs), consumer electronics, renewable energy storage, and industrial applications.
● Key Processes in a Battery Fabrication Line
1. Material Preparation
- Active Material Mixing: The active materials for electrodes (such as lithium compounds for cathodes and graphite for anodes) are mixed with binders and conductive additives to form slurries.
- Separator Production: Separators, which prevent short circuits between electrodes, are produced from materials like polyethylene or polypropylene.
2. Electrode Fabrication
- Coating: The slurry is coated onto metal foils (copper for anodes and aluminum for cathodes) using precision electrode calendering machines to achieve uniform thickness.
- Drying: Coated electrodes are dried in ovens to remove solvents, ensuring optimal performance characteristics.
- Calendering: The dried electrodes are compressed to enhance density and improve conductivity.
3. Electrode Cutting
- The dried and calendered electrodes are cut into specific dimensions suitable for the battery design.
4. Cell Assembly
- Layer Stacking or Winding: The anode, separator, and cathode are assembled by stacking or winding them together, depending on the cell design (cylindrical, prismatic, or pouch).
- Electrolyte Filling: The electrolyte is injected into the cell, saturating the electrodes and separator for optimal ion flow.
- Sealing: Cells are sealed to prevent leakage and contamination, often using heat sealing or ultrasonic welding.
5. Formation and Aging
- Formation Cycling: The cells undergo initial charging and discharging cycles to activate the electrochemical materials, stabilizing performance.
- Aging: Cells are aged in controlled environments to ensure consistent long-term performance.
6. Testing and Quality Control
- Performance Testing: Each battery is tested for key metrics such as capacity, internal resistance, voltage, and cycle life to ensure they meet specifications.
- Safety Testing: Rigorous safety tests, including thermal runaway, short-circuiting, and overcharging, are conducted to ensure compliance with safety standards.
7. Packaging and Shipping
- Once the batteries pass all quality checks, they are packaged and prepared for shipment to customers or distribution centers.
● Key Equipment in a Battery Production Line
1. Mixers: For preparing electrode slurries.
2. Coating Machines: For applying active material slurries onto metal foils.
3. Drying Ovens: To remove solvents from coated electrodes.
4. Calendering Machines: For compressing electrodes to desired specifications.
5. Cutting Machines: For precise sizing of electrodes.
6. Assembly Stations: For stacking or winding the electrodes, separators, and electrolytes.
7. Filling Machines: For injecting the electrolyte into the cells.
8. Sealing Equipment: To secure the cell and prevent leakage.
9. Testing Equipment: For performance and safety evaluations.
● Advantages of a Battery Production Line
1. Automation: High levels of automation improve efficiency, reduce labor costs, and minimize human error.
2. Scalability: Production lines can be scaled up or down to meet changing demand, making them flexible and adaptable.
3. Quality Control: Integrated testing and quality control processes ensure that only high-quality batteries reach the market, enhancing reliability and safety.
4. Cost Efficiency: Streamlined processes reduce production costs and waste, making it economically viable to produce batteries at scale.
● Applications of Batteries
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Batteries are a critical component, providing the energy needed for propulsion and energy recovery.
- Consumer Electronics: Used in smartphones, laptops, tablets, and wearable devices.
- Renewable Energy Storage: Batteries store energy from renewable sources like solar and wind, ensuring a stable energy supply.
- Industrial Applications: Employed in backup power systems, robotics, and various industrial equipment.
● Conclusion
A battery production line is essential for manufacturing various types of batteries efficiently and reliably. As the demand for batteries continues to grow, particularly with the rise of electric vehicles and renewable energy solutions, advancements in battery production technology will play a critical role in meeting global energy storage needs. The ability to produce high-quality, safe, and efficient batteries at scale will be a cornerstone of the transition to sustainable energy systems.
HOT PRODUCTS
-
 Automatic Cylinderical Battery Electrode Winding Machine
Read More
Automatic Cylinderical Battery Electrode Winding Machine
Read More
-
 100-200L Double Planetary Vacuum Mixing Machine for Lithium Battery Slurry
Read More
100-200L Double Planetary Vacuum Mixing Machine for Lithium Battery Slurry
Read More
-
 Large Heating Roller Press Machine Calender For Li ion Battery Production Line
Read More
Large Heating Roller Press Machine Calender For Li ion Battery Production Line
Read More
-
 Large 3 Rollers Battery Electrode Film Intermittent Coating Machine for Pilot Production Line
Read More
Large 3 Rollers Battery Electrode Film Intermittent Coating Machine for Pilot Production Line
Read More
-
 512 Channel 5V3A Battery Grading Machine/Battery Charge Discharge Machine Tester
Read More
512 Channel 5V3A Battery Grading Machine/Battery Charge Discharge Machine Tester
Read More


 cindy@tmaxcn.com
cindy@tmaxcn.com David@battery-equipments.com
David@battery-equipments.com Wechat:13506084915
Wechat:13506084915